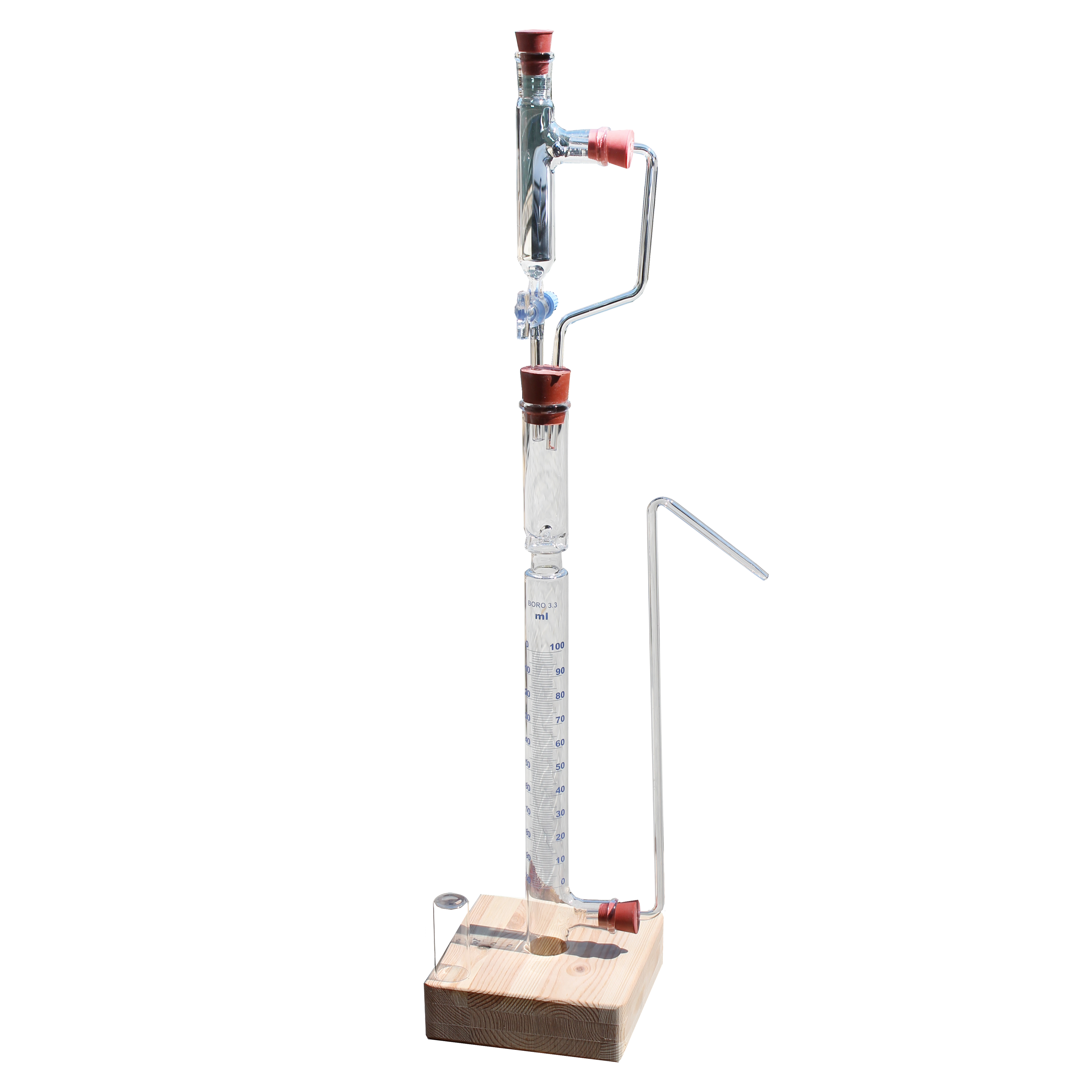
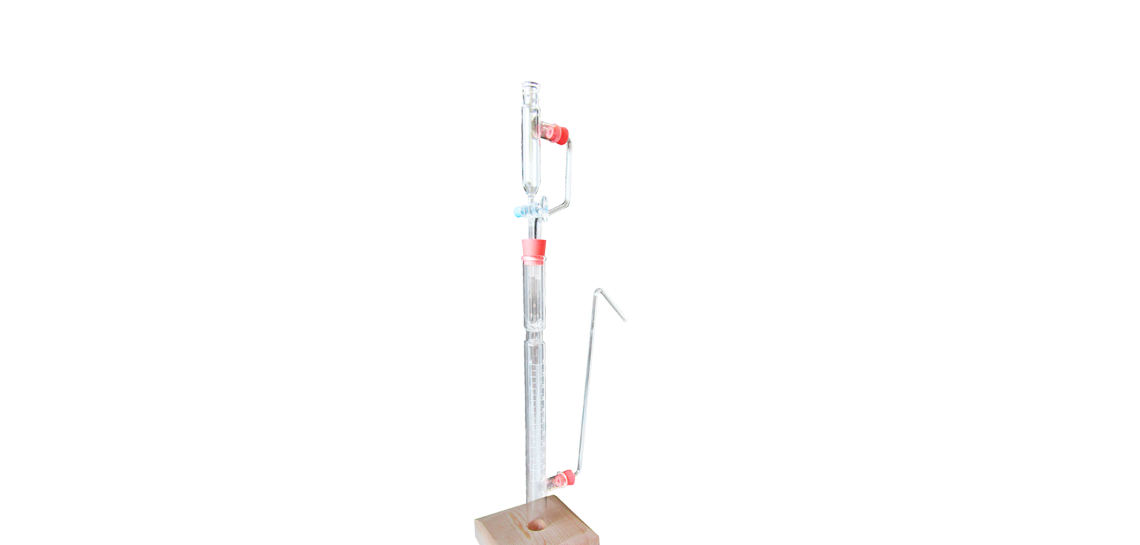
Pizzarelli Calcimeter
Instrument for the rapid % determination of the contents of calcium carbonate (CaCo3) in clays and marnes. The sample substance is placed in the test-tube, then put in the loading pipe some hydrochloric acid. The carbon dioxide formed by the reaction pushes the water of the graduated cylinder and you can directly read on the scale the quantity of carbonate originally present in the sample.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
• Made all glass with wooden base and screw blocking for glass parts
| Code | Model | External dimensions | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| GT0161 | PIZZARELLI CALCIMETER | 170x170x730 mm | 1,2 kg |
| Code | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|
| GT0152 | Loading pipe for Pizzarelli calcimeter | Open image |
| GT0153 | Graduated cylinder pipe for Pizzarelli calcimeter | Open image |
| GT0154 | Test-tube pipe for Pizzarelli calcimeter | Open image |
| GT0155 | Wooden base pipe for Pizzarelli calcimeter | Open image |
| GT0186 | vent pipe | Open image |
Related products
Dietrich-Fruhling Calcimeter
Description:
Instrument to determine the fast contents of CaCo3 (calcium carbonate) according to the method Dietrich-Fruhling.
Category:
CalcimetersStandard:
Laboratory:
Raw Materials LabInstrument to determine the fast contents of CaCo3 (calcium carbonate) according to the method Dietrich-Fruhling.
De Bernard Calcimeter
Description:
Instrument for the rapid % determination of the contents of calcium carbonate (CaCo3) as for DE BERNARD method.
Category:
CalcimetersStandard:
Laboratory:
Raw Materials LabInstrument for the rapid % determination of the contents of calcium carbonate (CaCo3) as for DE BERNARD method.
Scheibler Calcimeter
Description:
The Scheibler Calcimeter is designed on the basis of the volumetric measurement method to determine the percentage of carbonate in the soil. In this method,…
Category:
Chemical-Phisical Properties CalcimetersStandard:
Laboratory:
Raw Materials LabThe Scheibler Calcimeter is designed on the basis of the volumetric measurement method to determine the percentage of carbonate in the soil. In this method, the carbonate in the sample is converted into Co2 gas by adding hydrochloric acid and the resulting gas pressure.